Laser Wood Cutting Machine
Laser wood cutting machine remains a popular tool due to its precision, efficiency, and automation capabilities. While pulse arc welder is ideal for thin metal welding, and cheap stick welder is popular for at-home use, Laser wood cutting machine can cut wood of various shapes and sizes, reducing production costs. It's easy to operate and can achieve personalized, multifunctional cutting in line with users' diverse requirements. Moreover, its fast cutting speed and high efficiency can greatly improve production efficiency and economic benefits, making it a valuable addition to industrial use.
Types of welding are essential processes used in a wide range of industries, including construction, manufacturing, and automotive. Professionals and hobbyists alike have access to various types of welding equipment, each designed to suit different needs and applications. Some of the most common types of welding equipment include pulse arc welder, cheap stick welder, and Laser wood cutting machine. Pulse arc welder, for example, is highly effective for welding thin sheets of metal with precision. A cheap stick welder, on the other hand, is ideal for smaller at-home welding projects. Laser wood cutting machines are efficient and highly precise, making them a popular choice among carpenters and furniture makers due to their ability to accurately cut various shapes and sizes of wood, including curved and intricate designs. Overall, these welding equipment options offer users a myriad of choices to suit different needs and requirements.
PARAMETERS:
Name | ||||||||
Type | Vertical joint 6 degrees | |||||||
The main purpose | Laser Weld | |||||||
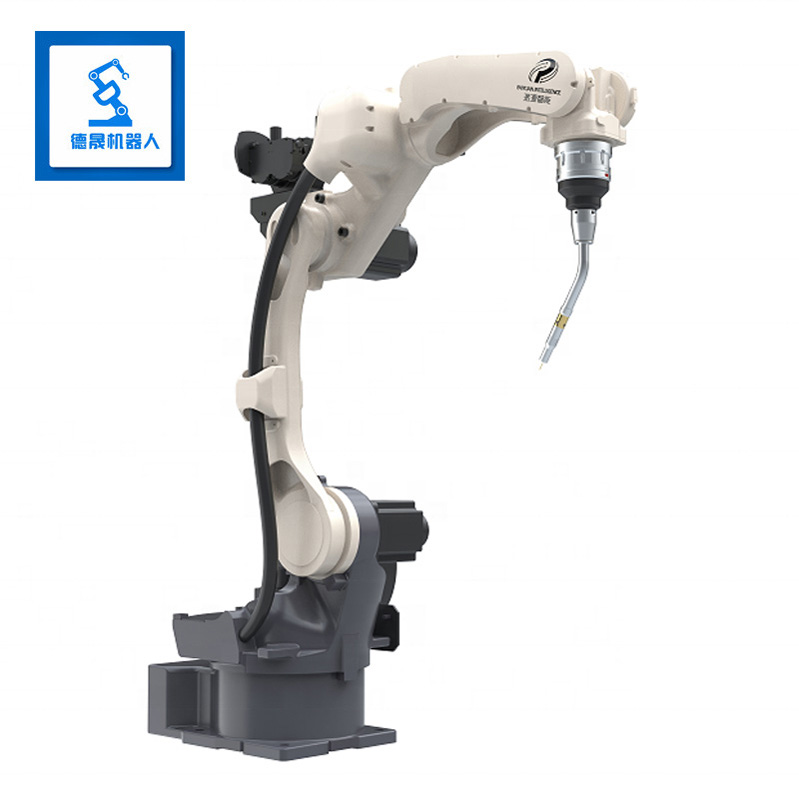
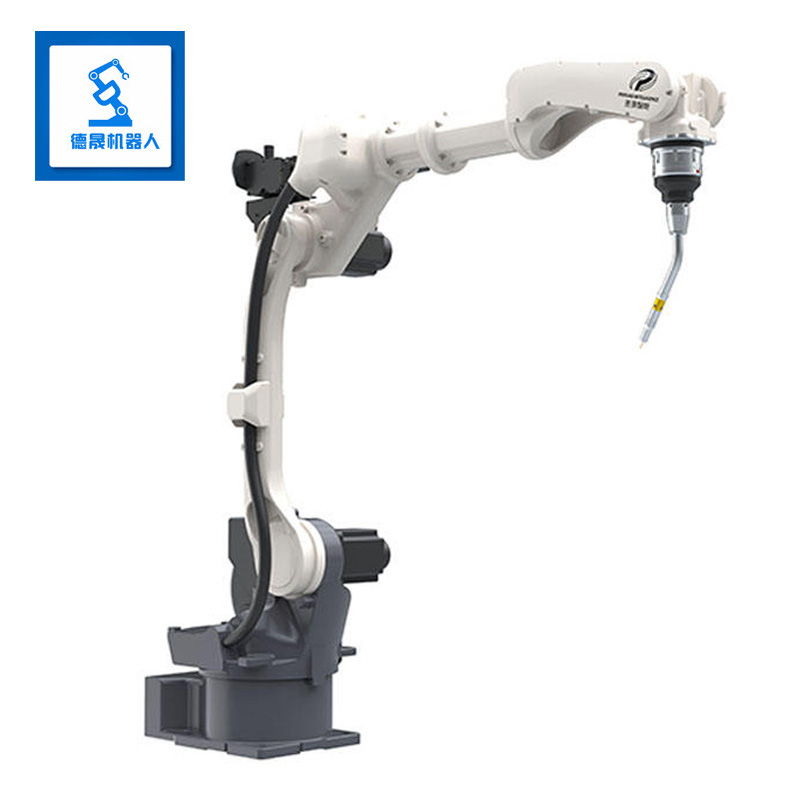
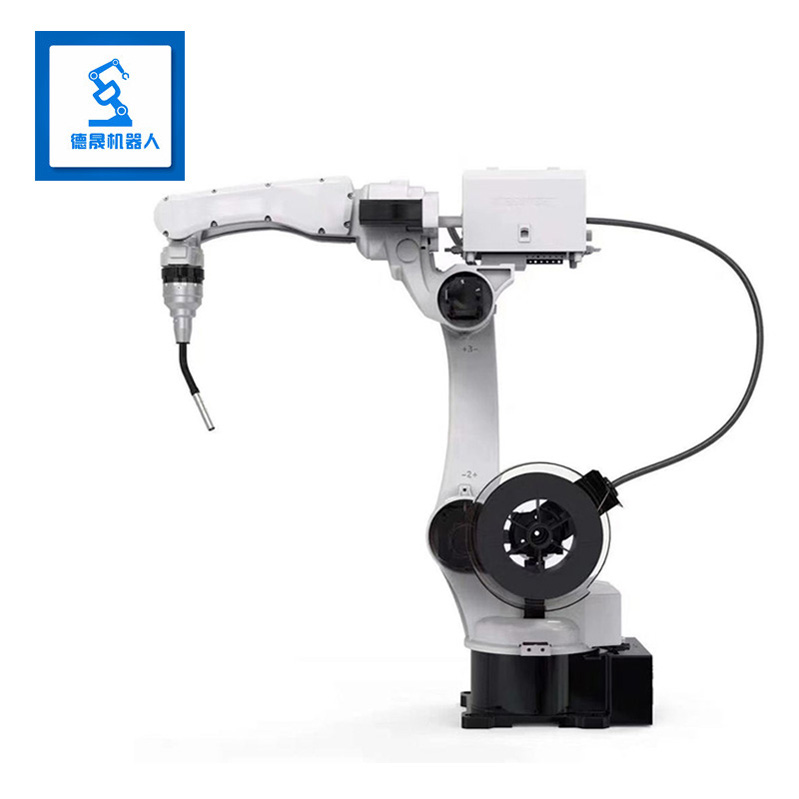
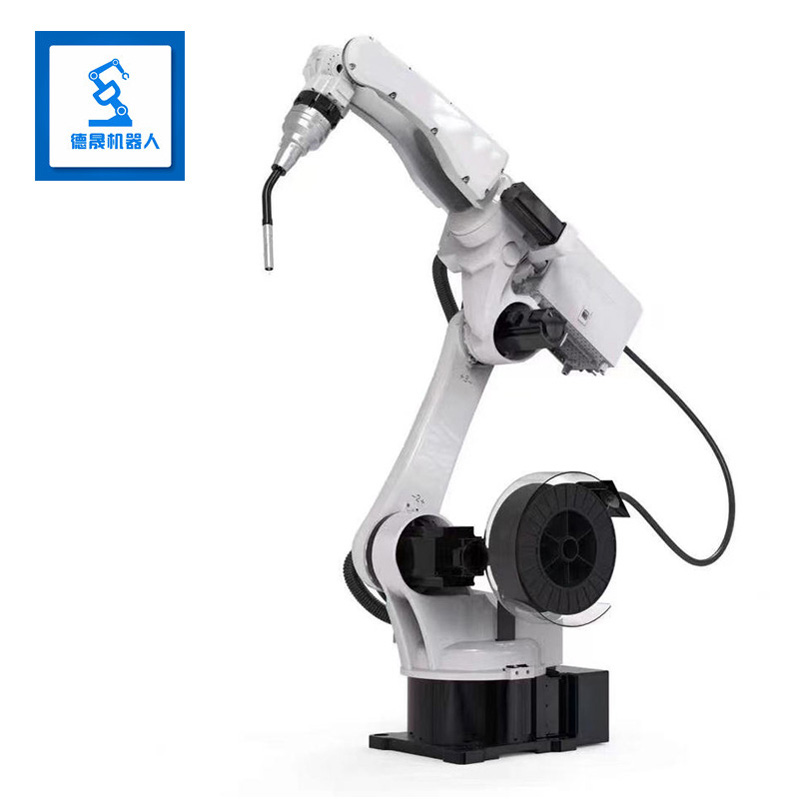
specification | BR10iG-14 | |||||||
Maxload weight | 10KG | |||||||
Position repeatability | 0.05mm | |||||||
Vibration | s4.9m/S | |||||||
Body weight | 149KG | |||||||
Maximum reach | 1566mm | |||||||
Conditions | 0-45RC,10-80%RH(no condensation) | |||||||
Protection class | Equivalent to lP65 | |||||||
Installation | Ground, hoisting side mounting | |||||||
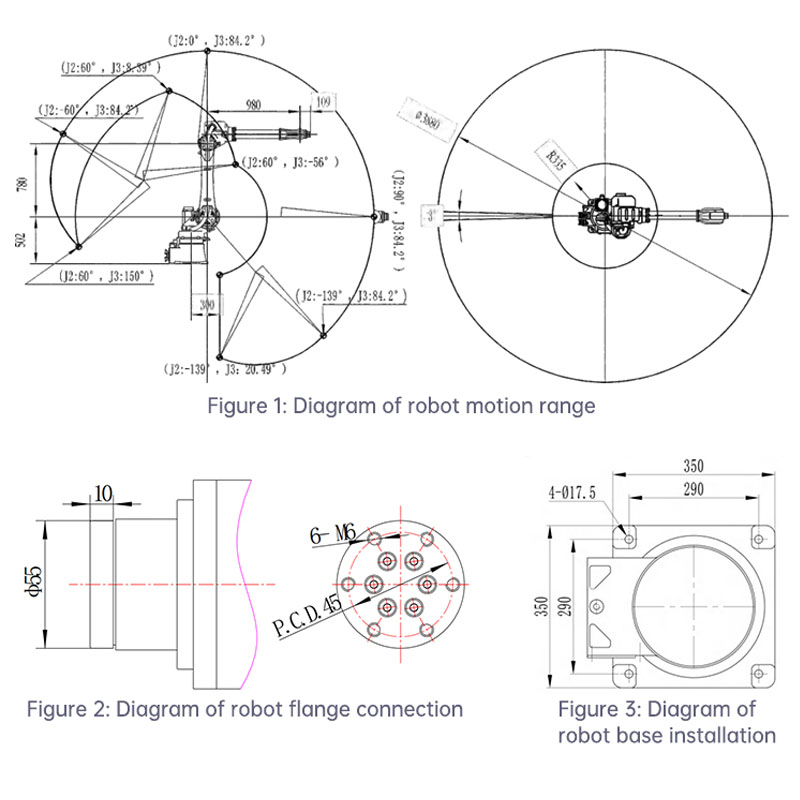
Range | basic | J1 | ±170° | Max | basic | J1 | 173.6°/S | |
J2 | +90°-160 | J2 | 138.8°/S | |||||
J3 | +115°-90 | J3 | 198.3°/S | |||||
arm | J4 | ±190° | arm | J4 | 288.1°/S | |||
J5 | ±140° | J5 | 400°/S | |||||
J6 | ±360° | J6 | 588.2°/S | |||||
DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS:
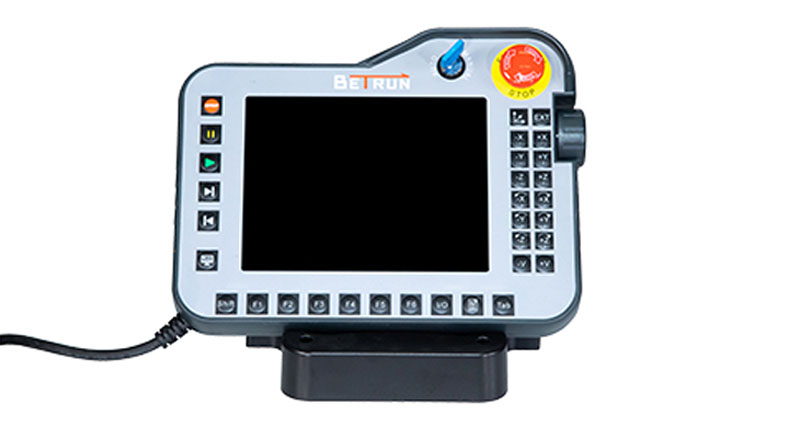
robot CONTROLSYSTEM:
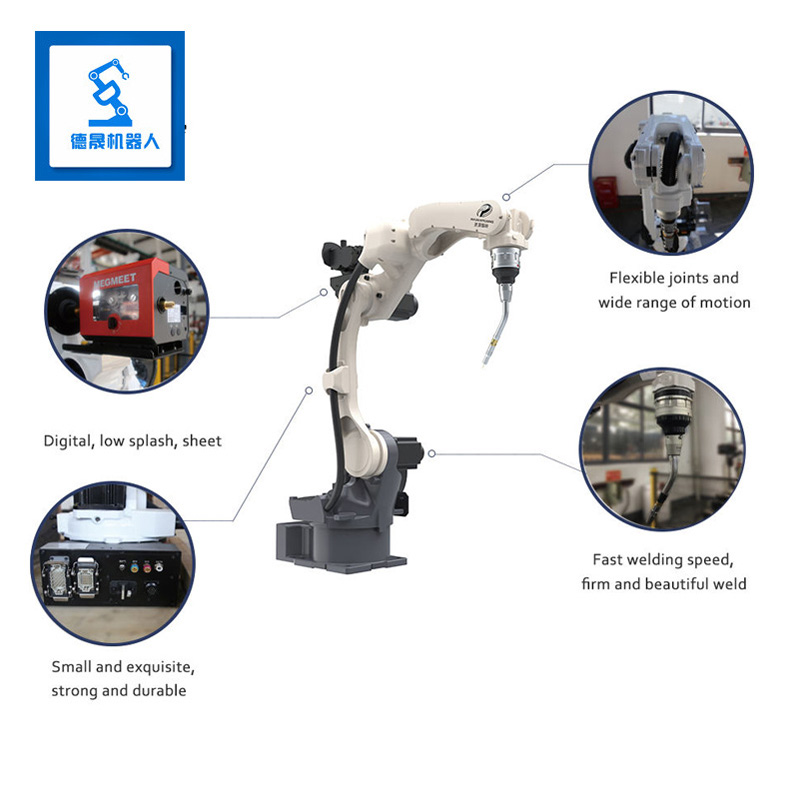
FEATRUES:
Arc welding robots come in two types, electrode and non-electrode, and are highly efficient with high stability. They use ac servo pressure technology and high precision reducers for low velocity stability and high speed dynamic response. Precise weld trajectory tracking technology, aided by laser and visual sensors, allows for optimal welding quality. The robot can coordinate movement with the positioner to maintain welding gun and workpiece position while avoiding collisions. These abilities allow it to perform high-productivity, high-quality welding operations for extended periods.
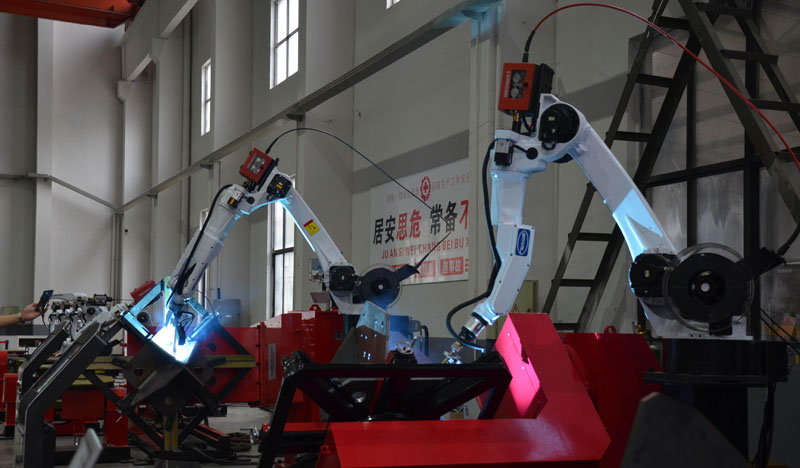
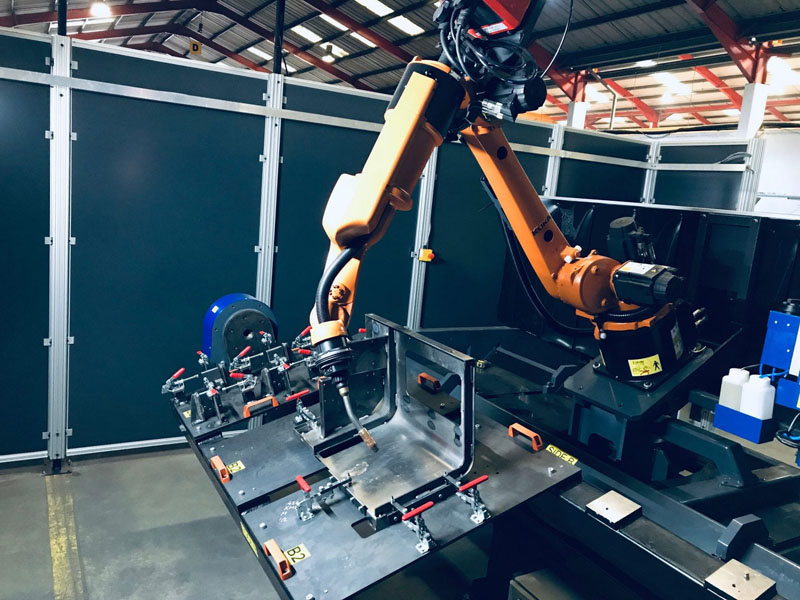
APPLICATIONS:
Welding robots are utilized in three main fields: workstation, production line, and automobile parts production. The workstation field requires coordination between the positioner and welding robot to achieve automatic welding, with seamless movement that meets the welding track, speed, and gun position requirements. In the production line field, the welding robot production reduces manpower costs and improves efficiency by connecting workpiece conveying lines to form a production line. Meanwhile, automobile parts production highly benefits from welding robots, especially in the automobile chassis welding process, where welding robot replaced earlier operations, improving both welding quality and operation time.
PACKAGE AND SHIPPING:
CERTIFICATIONS:
COOPERRATION PARTNER
EXHIBITION:
MORE PRODUCTS:
CONTACT US: